Tissue culture is a fascinating and powerful technique that has revolutionized the fields of medicine, biology, and biotechnology. Have you ever wondered how scientists grow cells outside of the body for research or medical purposes? In essence, tissue culture allows us to replicate and study living cells in a controlled environment. This article will help explain the process of tissue cultures using healthy cells, how it works, and its significance in the scientific world.
Whether you’re interested in the practical applications of tissue culture or simply curious about how this process is done, you’ll find all the details you need here. By the end, you’ll understand not just the steps involved, but also the immense impact this technology has on everything from disease research to agricultural improvements.
What is Tissue Culture?
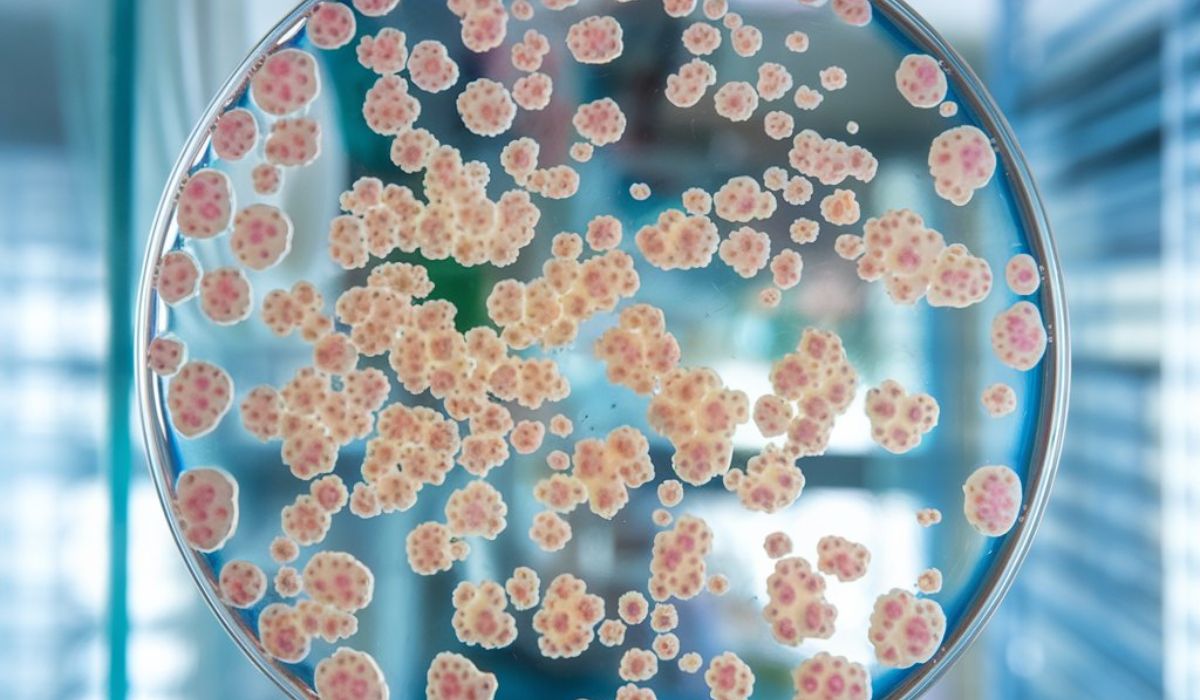
Tissue culture is the process of growing cells or tissues in a controlled, artificial environment outside of the organism’s body. Think of it like explain the process of tissue a miniature ecosystem where cells can thrive, multiply, and even differentiate into various types of tissues. This is made possible by placing cells into a sterile culture medium, where they receive nutrients and growth factors necessary for survival.
Tissue culture is essential in many fields such as medical research, cancer studies, and even plant propagation. It allows researchers to study diseases, test drugs, and explore biological functions without the need to use live animals.
Why Use Healthy Cells in Tissue Culture?
Using healthy cells is crucial for accurate and reliable results in tissue culture. Healthy cells are necessary to create viable cultures that can grow and behave like they would inside the body. When researchers use healthy cells, they can more effectively:
- Study natural cell behavior: Healthy cells are more likely to replicate and grow as expected.
- Ensure reproducibility: Cultures derived from healthy cells will produce consistent results across experiments.
- Reduce complications: Healthy cells are less likely to carry diseases or undergo genetic mutations that could affect the integrity of the study.
In other words, healthy cells serve as the “gold standard” for conducting research or growing tissues for practical use in medicine and agriculture.
Steps to Explain the Process of Tissue Cultures Using Healthy Cells
Tissue culture might sound complex, but in reality, it’s a well-organized series of steps. Let’s break down the entire process of tissue cultures using healthy cells:
- Collection of Tissue Sample: The first step in any tissue culture process is collecting the sample of healthy tissue or cells. This can be done from various sources such as animal tissues, human biopsies, or even plant cuttings. The type of tissue selected depends on the goal of the research or application.
- Sterilization: To prevent contamination by bacteria, fungi, or other microorganisms, the sample must be thoroughly sterilized. This is usually done using chemicals like alcohol or by exposing the sample to heat or ultraviolet (UV) light.
- Isolation of Cells: Once sterilized, the tissue sample is then broken down into smaller pieces, and individual cells are isolated. This can be achieved using enzymes that break down the extracellular matrix, which binds the cells together.
- Placing Cells in Culture Medium: The isolated cells are then transferred to a petri dish or culture flask filled with a specially formulated nutrient-rich medium. This medium provides the cells with essential nutrients, growth factors, and hormones necessary for growth.
- Incubation: The cultures are placed in an incubator, where temperature, pH, and humidity levels are carefully controlled. This helps mimic the conditions inside the body, encouraging cells to grow and divide.
Preparing the Cells for Culture

Before tissue cultures using healthy cells can begin, proper preparation is essential. First, the tissue must be carefully collected, usually under sterile conditions to prevent contamination. Once collected, the tissue may be cleaned and treated with enzymes (such as collagenase or trypsin) to break it down into a single-cell suspension.
This step is important because it allows individual cells to be isolated from the surrounding tissue, enabling them to thrive independently in the culture medium. The healthy cells are then ready for the next stage of the process.
Sterilization Techniques in Tissue Culture
Sterilization is a crucial aspect of tissue culture. The goal is to eliminate any external contaminants that could interfere with the cell growth process. Common sterilization methods include:
- Alcohol (Ethanol): A commonly used disinfectant to clean tools, surfaces, and sometimes the tissue sample itself.
- Autoclaving: This process uses high pressure and temperature to sterilize culture media, glassware, and equipment.
- UV Radiation: Ultraviolet light is used to sterilize the air, surfaces, and sometimes the culture media in the incubators.
Sterilization prevents any unwanted bacteria or fungi from infecting the culture and affecting the growth of healthy cells.
Choosing the Right Culture Medium
The culture medium is the lifeblood of any tissue culture. It’s a special solution that contains all the nutrients, vitamins, amino acids, and hormones the cells need to grow. For tissue cultures using healthy cells, different media are used depending on the type of cells being grown.
- Basal Media: Contains essential nutrients like glucose, amino acids, vitamins, and minerals for basic cell survival.
- Supplemented Media: Often include additional growth factors or hormones to encourage cell growth, division, and differentiation.
The right medium ensures the cells can thrive and reproduce, enabling the tissue culture process to proceed smoothly.
Incubation and Growth of Cells
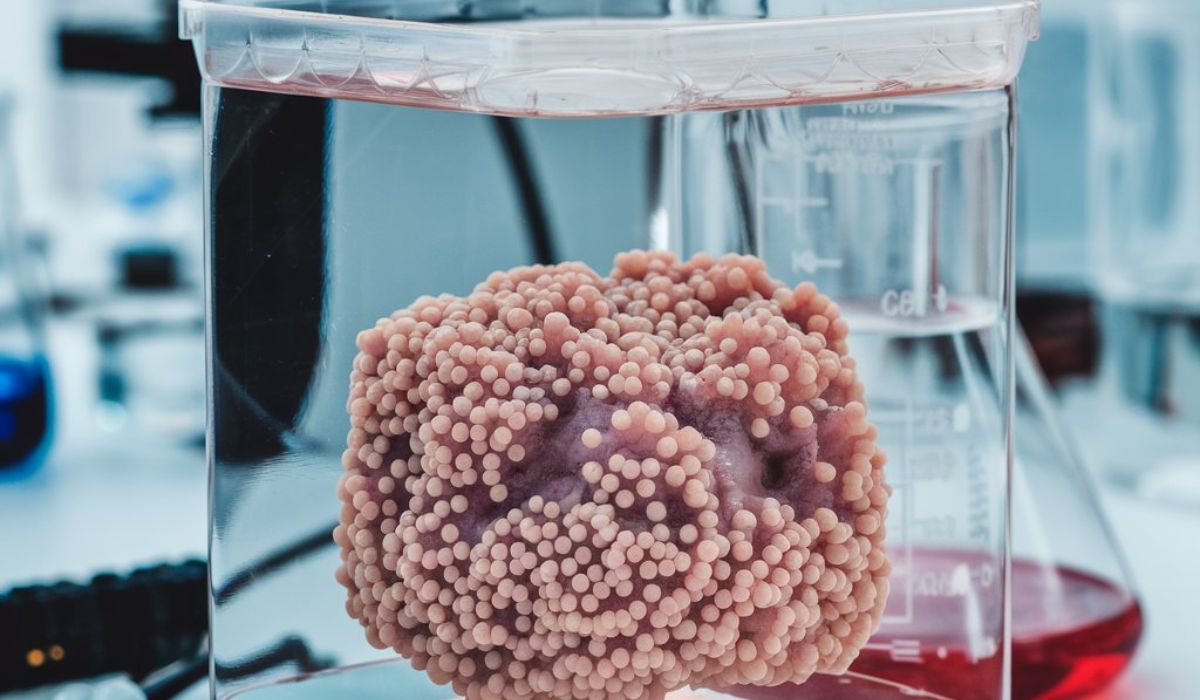
Once the cells are placed in the culture medium, they need to be incubated in conditions that mimic the body. Tissue cultures using healthy cells are usually incubated at a temperature of around 37°C (98.6°F) in a CO2-controlled incubator. This simulates the environment of the human body, providing the cells with the warmth and gas balance they need to survive and grow.
As the cells continue to grow, they start to divide and form a monolayer of cells that spreads across the surface of the culture dish or flask.
Monitoring and Maintaining Healthy Cells
After the cells begin to grow, it’s important to monitor their health and viability. Researchers check the cultures regularly for signs of contamination, cell death, or abnormal growth. Healthy cells that are maintained in optimal conditions should continue to grow and divide without any significant issues.
Key factors to monitor include:
- Cell density: Cells can only grow up to a certain density before they need to be subcultured (divided into new containers).
- pH of the medium: The medium’s pH can drop due to cell metabolism, so it’s essential to regularly check and adjust it.
- Contamination: Any unwanted growth of bacteria, fungi, or mold must be addressed immediately to prevent compromising the culture.
Subculturing and Passaging Cells
As the cells grow, they eventually need to be transferred into fresh culture medium. This process is known as subculturing or passaging. It involves gently separating the cells from the surface of the culture dish and transferring them to a new dish with fresh medium. This helps maintain healthy growth conditions and prevents overcrowding.
Applications of Tissue Culture with Healthy Cells
Tissue cultures using healthy cells have a wide range of applications across various fields:
- Medical Research: Understanding diseases like cancer, AIDS, or Alzheimer’s through cell-based models.
- Drug Testing: Testing the effects of new drugs or chemicals on cells before clinical trials.
- Gene Therapy: Cells can be modified to study genetic diseases or develop therapies.
- Plant Tissue Culture: Cloning plants and studying their genetics for agricultural improvements.
Challenges in Tissue Culture
While tissue culture has many advantages, it also comes with challenges:
- Contamination: Even with sterilization techniques, bacteria, fungi, or viruses can sometimes contaminate cultures.
- Cell Senescence: Cells can only divide a certain number of times before they stop growing, which limits the lifespan of some cultures.
- Cost and Complexity: Tissue culture requires specific equipment, sterile environments, and expertise, making it costly and complex.
Advancements in Tissue Culture Technology
Advancements in tissue culture technology, such as 3D cultures and organoids, have made the process even more sophisticated. These technologies mimic the three-dimensional structure of real tissues, providing more accurate models for research and drug testing.
Ethical Considerations in Tissue Culture
Tissue culture raises ethical questions, especially when it comes to the use of human or animal cells. It’s important for researchers to follow ethical guidelines and ensure that tissues are obtained with proper consent.
Tissue Culture vs. Organ Transplants
Unlike organ transplants, which involve replacing entire organs, tissue culture focuses on growing and studying individual cells. However, tissue culture research has made significant contributions to improving organ transplant procedures by allowing for better tissue compatibility testing.
Future of Tissue Culture Using Healthy Cells
Looking ahead, tissue culture techniques continue to evolve. With the help of modern technology, the future of tissue culture holds great promise for advancing medical treatments, improving drug discovery, and even creating tissues or organs for transplantation.
FAQs
What is tissue culture?
Tissue culture is the process of growing cells or tissues in a controlled, artificial environment outside the organism’s body.
Why is it important to use healthy cells in tissue culture?
Healthy cells ensure accurate results, consistency, and the ability to study natural cell behavior without interference from diseases.
Can tissue cultures be used for drug testing?
Yes, tissue cultures are commonly used in drug testing to study the effects of chemicals and medications on living cells.
How are tissue cultures maintained?
Tissue cultures are maintained by providing cells with nutrients in a sterile environment, adjusting pH levels, and regularly subculturing the cells.
What are some applications of tissue culture?
Tissue cultures are used in medical research, drug testing, gene therapy, plant cloning, and more.
For More Visit, rankshort
